The commentsarea plugin¶
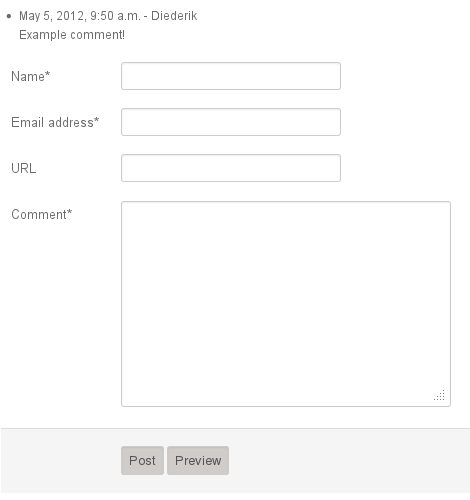
The commentsarea plugin displays the form and messagelist that django-contrib-comments (or django.contrib.comments) renders.
The displays a list of comments, with a comments area below:
By default, the displayed comments will look very plain. This is however, not an accident. The django.contrib.comments module provides these defaults to make it fully customizable to the design and workflow of the web site where it is being used. Hence, this plugin depends on a properly configured django.contrib.comments module.
Tip
For an advanced plug&play setup, you can use the django-fluent-comments application which includes features such as Ajax-based posting. Make sure to include it’s JavaScript and CSS files somewhere in the page.
Installation¶
Add the following settings to settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS += (
'django_comments',
'fluent_contents.plugins.commentsarea',
)
The django.contrib.comments module also requires a location for it’s pages.
Add the following to urls.py:
urlpatterns += [
url(r'^blog/comments/', include('django_comments.urls')),
]
This URL can be anything off course, like /comments/, /respond/comments/ or /blog/comments/ for example.
Note
As of Django 1.8, the django.contrib.comments module is no longer bundled with Django. It’s provided as separate application that can be installed from PyPI.
For older Django projects, replace django_comments with django.contrib.comments in the example above.
Configuration¶
After the installation, each page can be enriched with a comments area.
Posting a comment however, produces an almost blank page.
That’s because comments/base.html should be overwritten.
To get a usable comments module, the least you need to do, is providing two templates:
comments/base.htmlcomments/posted.html
Note
As with other plugins of django-fluent-contents, the output of the plugin is cached.
Only when a comment is posted, the output will be refreshed. To change templates in a development/runserver
environment, set FLUENT_CONTENTS_CACHE_OUTPUT to False in the settings.
The base.html template¶
The comments/base.html template is used by every template of the comments module.
It needs to provide two blocks;
- title: the sub title to display in the
<title>tag. - content: the content to display in the
<body>tag.
These blocks can be mapped to your site template. It’s contents could be something like:
{% extends "mysite/base.html" %}{% load i18n %}
{% block headtitle %}{% block title %}{% trans "Responses for page" %}{% endblock %}{% endblock %}
{% block main %}
<div id="content" class="clearfix">
{% block content %}{% endblock %}
</div>
{% endblock %}
The comments/base.html file can be stored in the templates folder of your site theme.
The posted.html template¶
The final “Thank you for posting” page is also quite plain.
Replace it be something more fresh by overriding the comments/posted.html template.
For example, try something like:
{% extends "comments/base.html" %}{% load i18n %}
{% block title %}{% trans "Thanks for commenting" %}{% endblock %}
{% block extrahead %}
{{ block.super }}
<meta http-equiv="Refresh" content="5; url={{ comment.content_object.get_absolute_url }}#c{{ comment.id }}" />
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<h1>Thank you for responding</h1>
<p>
We have received your comment, and added it to the web site.<br />
You will be sent back to the article...
</p>
{# Using identical formatting to normal comment list #}
<dl id="comments">
<dt id="c{{ comment.id }}">
{{ comment.submit_date }} - {{ comment.name }}
</dt>
<dd>
<p>{{ comment.comment }}</p>
</dd>
</dl>
<p><a href="{{ comment.content_object.get_absolute_url }}#c{{ comment.id }}">Back to the article</a></p>
{% endblock %}
The template now contains links back to the blog page, and no longer appears as dead end. It will automatically redirect back to the blog in a few seconds.
Additional configuration¶
The django.contrib.comments module can be further extended with other modules. In fact, django.contrib.comments only establishes a standard methodology for integrating comments to a Django site. The framework also supports moderation, flagging, and RSS feeds too. More documentation can be found at:
- Django’s comments framework
- Customizing the comments framework
- Example of using the in-built comments app
Some Django applications already implement these features. For example:
- django-fluent-comments, which includes:
- Ajax-based previews and posting of comments.
- Comment moderation, and Akismet based filtering.
- E-mail notifications.
- django-threadedcomments
These modules can enhance the commentsarea even further.